Are you struggling to track the impact of your Facebook ads? Wondering which Facebook attribution model to use?
In this article, you'll discover seven different Facebook ad attribution models to assess your campaigns' performance.

About Facebook Attribution Models
The Facebook attribution tool gives you insights into your customers' purchasing journey and the roles of different touchpoints along the conversion path. This information can help you identify potential tweaks you can make to optimize the ads you're running.
Facebook allows you to choose which metrics and touchpoints you want to consider when looking at ad performance. Once you know what you're looking for, you can begin the process of setting up an attribution window and determining which touchpoints to consider. How you decide which Facebook attribution model to use will depend on what you're selling and what your goals are.
As part of this process, you may want to understand how people interact with your ads. Questions like how many people have seen the ad (impressions) and taken action on the ad (conversions—purchases, etc.) may come to mind.
If you're running an eCommerce store, Facebook advertising will play a crucial role in generating business. Understanding the different Facebook attribution models and how they work will help you closely track your campaigns and see how your customers are interacting with your ads.
How to Set Up the Facebook Attribution Tool
To set up the Facebook attribution tool, you need to have a Facebook Business Manager account. If you haven't already set one up, head to the Facebook Business Manager page and click Create Account. Then follow the prompts to provide your business details and create your account.
When you're finished, go to your Attribution dashboard and click Get Started. You'll then be asked to select your type of business. Your options are Single Business; Separate Brands, Vertical or Regions; or Agency.
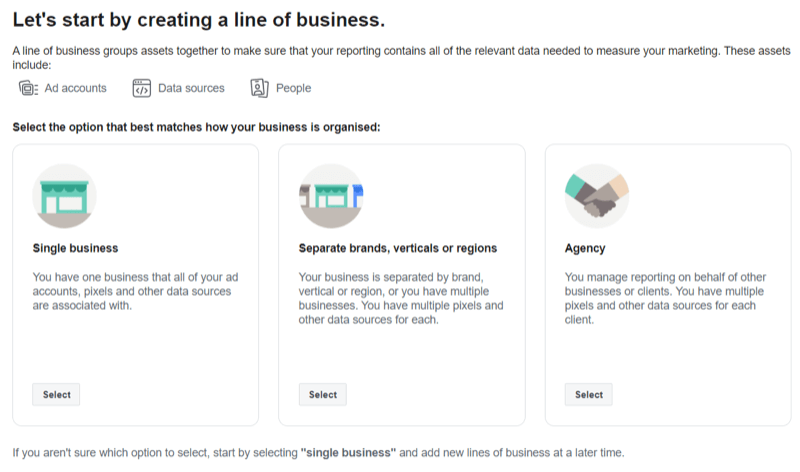
Once you've chosen a business type, you're taken to a page where you can sync your ad accounts with Facebook Business Manager. Add the data sources for your ad accounts, add the people who have administrative rights for your ad campaigns, and set the applicable time zone and currency. This article walks you through the process of assigning people and assets.
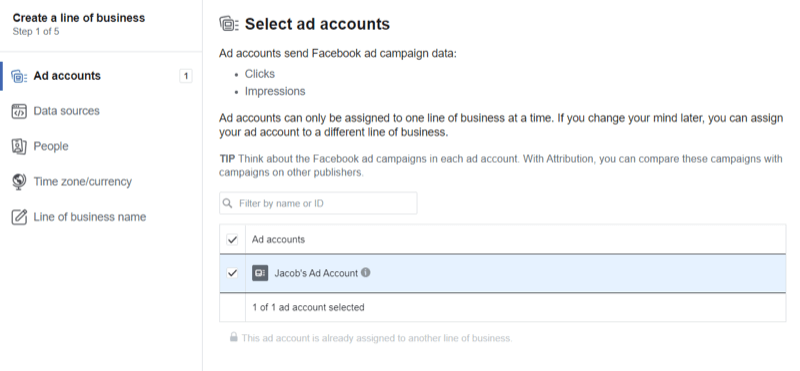
The attribution tool will now sync all of the data from your Facebook pixel. This process can take a couple of hours so be prepared to wait.
Get World-Class Marketing Training — All Year Long!
Are you facing doubt, uncertainty, or overwhelm? The Social Media Marketing Society can help.
Each month, you’ll receive training from trusted marketing experts, covering everything from AI to organic social marketing. When you join, you’ll also get immediate access to:
- A library of 100+ marketing trainings
- A community of like-minded marketers
- Monthly online community meetups
- Relevant news and trends updates
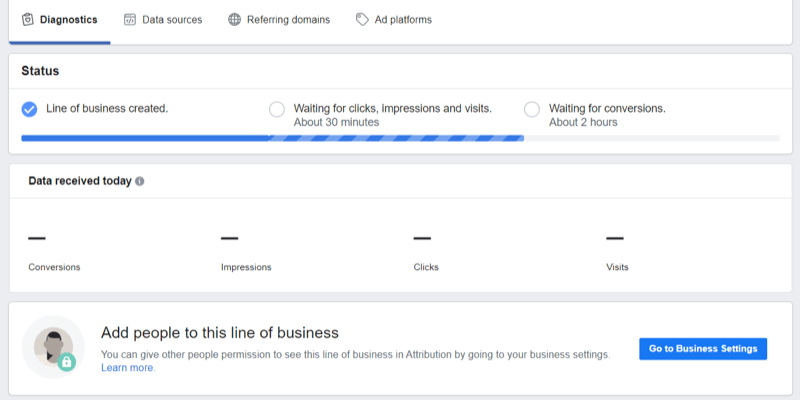
Once Facebook has received your data, you'll notice a green tick box with the message “Data Is Being Received.” In the image below, we were testing a new ad account so the data fields are blank.
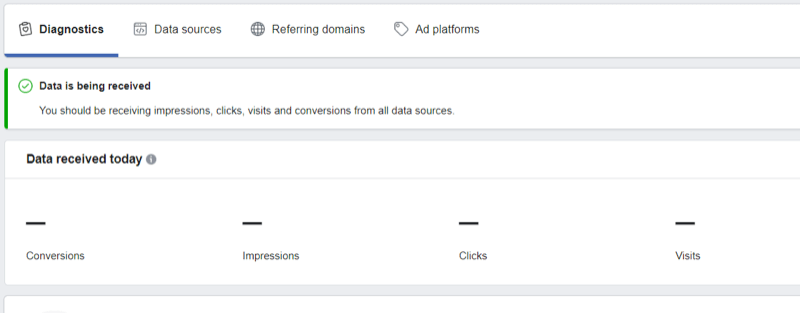
Once the data from your Facebook pixel has been synchronized, select the conversion event you want to analyze from the drop-down menu in the top-right corner of the screen. You can choose any conversion you've previously set up or create a new one.
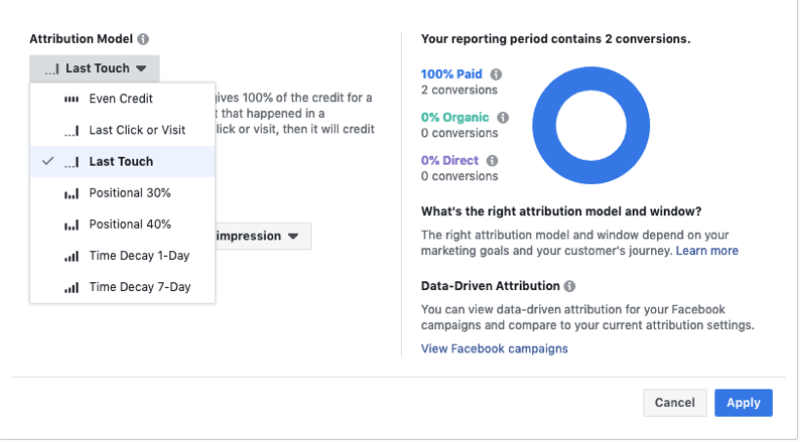
Once you've selected your conversion, the next step is to choose one of the following attribution models:
- Even Credit
- Last Click or Visit
- Last Touch
- Positional 30%
- Positional 40%
- Time Decay 1-Day
- Time Decay 7-Day
Each attribution model has its pros and cons (as I discuss in detail in the next part of this article). The one you choose will depend on what type of business you're running and what you want to achieve with your Facebook ad campaigns.
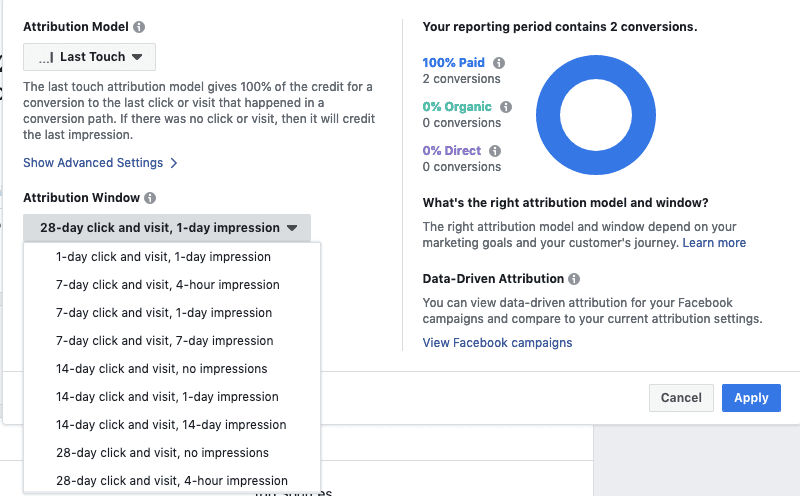
After you've selected an attribution model, choose the attribution window you want to use. You can choose from 17 different attribution windows, which can be a little overwhelming at first. The default setting is “28-Day Click and Visit, 1-Day Impression.” This means that Facebook credits actions that were taken within 28 days of clicking your ad and within 1 day of viewing your ad.
If you're unsure of which attribution window to select, here's my advice:
- If your product is at a lower price point or the buying cycle of your product is short, stick with the default setting.
- If your product is high-ticket and has a longer customer buying journey, go with one of the lengthier options.
Once you make your selections and click Apply, you'll start seeing your analytics and the results that your Facebook pixel has tracked based on the attribution model and window you selected.
Now let's dive in for a more in-depth look at what Facebook attribution models are and the pros and cons of each type.
#1: Even Credit Attribution Model
The even credit attribution model gives you a holistic view of a customer's journey. Credit is given to each touchpoint a customer interacts with before a conversion happens. The even credit attribution model helps you understand the different ways someone has interacted with your ad.
You'll get insight into the first touchpoint that introduced a person to your ad, the middle touchpoint that built consideration, and the final touchpoint that resulted in the person taking action, potentially leading to a conversion.
To visualize this, suppose a customer's conversion path looks like this:
Ad Impression > Ad Click > Visit > Ad Impression
With the even credit attribution model, each touchpoint would receive 25% credit for the conversion.

Discover Proven Marketing Strategies and Tips
Want to go even deeper with your marketing? Check out the Social Media Marketing Podcast! Publishing weekly since 2012, the Social Media Marketing Podcast helps you navigate the constantly changing marketing jungle, with expert interviews from marketing pros.
But don’t let the name fool you. This show is about a lot more than just social media marketing. With over 600 episodes and millions of downloads each year, this show has been a trusted source for marketers for well over a decade.
There's one catch, however. If the ad click and visit happen within 60 seconds of one another, both steps will be counted as the same touchpoint and only the ad click will be credited.
When Should I Use the Even Credit Attribution Model?
Use this model when you want a clear understanding and overview of the entire conversion path to see how customers and prospects interact with your Facebook ads.
#2: Last Click or Visit Attribution Model
As the name suggests, the last click or visit attribution model considers only the last click or visit in a conversion path. Facebook will recognize the last ad click or last visit as the final touchpoint so the last ad impression won't get credit for the conversion.
One of the downsides of the last click or visit attribution model is that it gives too much credit to the final steps in a conversion path and not enough insight into other important touchpoints that occurred in the conversion path.
When Should I Use the Last Click Attribution Model?
The last click attribution model is useful if you have a shorter sales cycle or you're looking at a buyer's final actions before making a purchase. If you want to look at the entire conversion path, the even credit, positional, or time decay attribution model is a better option.
#3: Last Touch Attribution Model
Similar to the last click model, the last touch attribution model should be used when you only want to consider the final touchpoints that caused your customer to convert. While this model can be valuable, it's important to remember that it gives no credit or insight into other touchpoints that could have impacted the customer's decision to convert.
When Should I Use the Last Touch Attribution Model?
The last touch conversion path is useful if you're selling a product that doesn't involve much buying consideration and you don't need to understand the whole conversion path.
#4 and #5: Positional 30% and Positional 40% Attribution Models
The positional 30% and positional 40% attribution models work in a slightly different way than the other models we've looked at.
With the positional 30% model, Facebook gives 30% of the conversion credit to the first touchpoint and 30% of the credit to the last touchpoint in the conversion path. The remaining credit (40%) is distributed among the other touchpoints in the conversion path. This model gives the middle touchpoints less credit than the first or final touchpoint in the conversion path.
The positional 40% attribution model works in the same way. The only difference is that 40% of the conversion credit is given the first and last touchpoints in a conversion path instead of 30%.
As with the other models, if a click and visit happen within 60 seconds of one another, only the click is credited. A positional attribution model works best if your business model or advertising objectives value first and last customer interactions more than the middle interactions.
When Should I Use a Positional Attribution Model?
Use this type of attribution model if you want to see which touchpoint drew the customer's attention to your ad and which touchpoint caused the conversion. This attribution model also credits the touchpoints that helped nurture your customers toward a decision so you can see where you need to focus your efforts in the future.
#6 and #7: Time Decay 1-Day and 7-Day Attribution Models
The time decay 1-day and 7-day attribution models are multi-touch models that give a portion of credit to all of the channels that led to a customer converting.
Let's say your customer sees a Facebook ad for your product on Tuesday. The next day, she remembers seeing your ad and goes directly to your website without making a purchase. A couple of days later, while browsing Instagram, the customer sees an ad for your product again. This time, she clicks on the ad and makes a purchase.
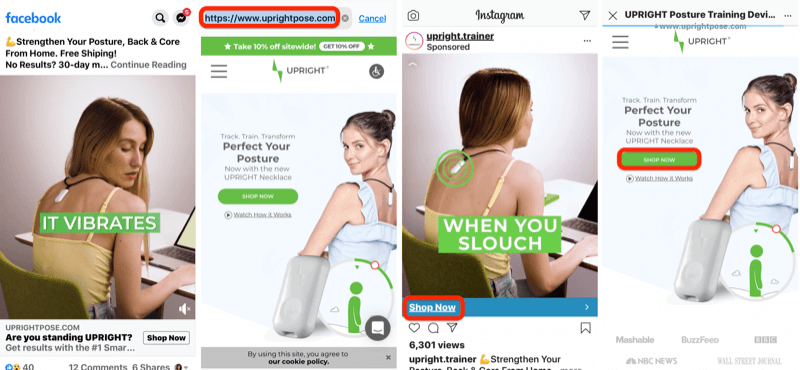
Each of these touchpoints would get some credit for the conversion but Instagram would get the most because it's the most recent channel the customer interacted with. Your Facebook ad would get the least amount of credit because it's the channel that the customer interacted with the furthest back in time.
The time decay 1-day model credits a conversion using a 1-day half-life. This means the touchpoints the customer interacted with 1 day before the conversion get 50% or more of the credit, while the touchpoints the person interacted with 2 days before the conversion receive up to 25% of the credit. The breakdown of the percentages will depend on how many touchpoints the customer interacted with leading up to the conversion.
With the time decay 7-day attribution model, the channels the person interacted with 7 days before the conversion receive 50% or more of the credit, while any channels they interacted with 14 days before the conversion receive up to 25% of the credit for each channel.
When you compare a time decay attribution model to the last touch or last visit model, the time decay model gives a better indication of how all of the different touchpoints contributed to a conversion.
When Should I Use a Time Decay Attribution Model?
A time decay model works well if you're running a time-sensitive promotional campaign. It will give you insights into how your customers behave when you run a promotion or offer, and if this behavior differs from other patterns or metrics you've noticed.
Because a time decay model credits every touchpoint, it works well if you're running a store with a large number of repeat purchasers. As these buyers are exposed to different advertising and marketing methods, a time decay attribution model can help you see what's driving repeat purchases.
Conclusion
Hopefully, this guide has given you a better understanding of the different types of Facebook attribution models and when to use them. Each model has its own way to measure the touchpoints on a conversion path. Deciding which model is best for your purposes will depend on your business and goals.
If you're running any type of eCommerce store, remember that attribution modeling is helpful if you're looking into how your customers interact with your ads and how they decide to take action on your offer.
What do you think? What's your favorite Facebook attribution model? Which attribution model would work best for your business? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
More articles on Facebook advertising:
- Discover six Facebook advertising mistakes and how to fix them.
- Learn how to create three custom reports in Ads Manager to help you quickly analyze your Facebook ad performance.
- Find out how to use Facebook ads to generate sales and leads quickly.
Attention Agency Owners, Brand Marketers, and Consultants

Introducing the Marketing Agency Show–our newest podcast designed to explore the struggles of agency marketers.
Join show host and agency owner, Brooke Sellas, as she interviews agency marketers and digs deep into their biggest challenges. Explore topics like navigating rough economic times, leveraging AI, service diversification, client acquisition, and much more.
Just pull up your favorite podcast app, search for Marketing Agency Show and start listening. Or click the button below for more information.

